The Yamnaya Culture
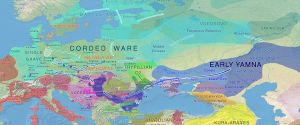
The Yamnaya are generally believed to have originated on the Volga Don Steppes, near the Volga River. This was first suggested by Nikolai Merperts. I. V. Sinitsyn excavated a series of barrows on the eastern side of the Volga River, between Saratov and Volgograd in modern day Russia, from 1951 to 1953. Based on analysis of pottery found in the lowest (and therefore oldest) graves, the Yamnaya are most likely of Repin and Kvalynsk origins. The pottery of Repin origin was found in barrows from the Don and middle Volga region. Pottery of Kvalynsk origin is found in barrows on the lower Volga River. This style eventually came to replace the Pottery of Repin origin. Daggers and sleeved axes, however show Miakop-Novosobodnaya influence. The Yamnaya spread out from this area relatively rapidly onto the Pontic Caspian Steppe, between 3400 and 2800 BC. Most of the pre-existing people’s persisted until around 2800 BC, at which time most have left the archaeological record, having been absorbed by the Yamnaya.[1][2]
Culture
Lifestyle

The Yamnaya were a group of prehistoric people who lived on the Pontic Caspian Steppe from 3000 to 2500 BC, during the late Copper Age on into the Bronze Age. They lived as nomadic or semi nomadic herders, traveling the grasslands in wagons and on horseback, this allowed them to access more and better grass for their herds of cattle and sheep. This in turn allowed them to acquire more wealth in the form of livestock and thereby become one of the most dominant people of their time.[1]
Diet
Their diets consisted mainly of meat (mostly beef, mutton, and pork, but also horse and wild game) along with dairy products like cheese, yogurt, and butter. Evidence for grain is scarce but not completely absent, wheat, amaranth, and millet were the most common grains consumed. Honey and Mead were most likely included, along with wild fruits and plants.[1][3]
Language
The Yamnaya are generally considered to be the fathers of the Proto Indo, European language, which evolved into the Indo European language family. This language family accounts for around 6% of all spoken languages today (445– 449 of the current 7000 languages spoken) but around 3 billion people speak a Proto Indo European language (45–46% of the world’s population).[2]
Burial Customs
They buried certain of their dead in pits covered by a mound of earth, called a barrow or kurgan. This is the origin of their name : Yamnaya, which comes from a Russian adjective “ Yamna” meaning “related to or concerning pits“.
There were three types of graves used
1.Pit Graves, a simple pit covered with branches or large flat stones. These are the earliest graves.
2.Catacomb Graves similar to pit Graves, but with “rooms” or “chambers” branching off of the main grave. These originate from the middle bronze age.
3.Timber Graves, these graves have a small house like structure, built over them, usually of branches and small trees, sometimes of bundles of reeds. These are the latest Graves.
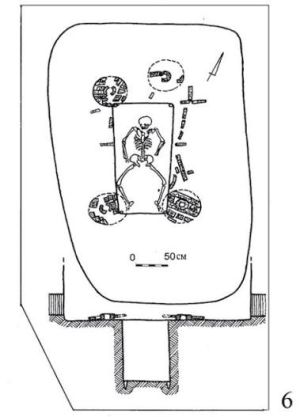
Individuals buried in these graves are generally considered to be of higher status, and usually are lying on their back with their knees raised and their head facing east. They are often laying on mats made of reads, sometimes these are painted. The floor and or the body is often covered in red ocher dust. They are generally buried with grave goods such as daggers axes, pestles,flint arrowheads, pottery, knives, animals, and even wagons.The graves are covered with a mound, and these may include rings of stone. The Earthen mounds raised over the graves are generally 30 to 40 foot wide, but can be as wide as 120 foot, and up to 12 foot high.[1][2]
Migrations
As a nomadic people, they left their mark, genetically and linguistically on many places and peoples, including Europe, western China and India, among others. Groups migrating into Europe, mixed with the European Neolithic farmers, and this eventually led to the formation of the Bell Beaker and Corded Ware Cultures. The Yamnaya are responsible for introducing the R1B Y haplogroup being introduced into Europe. The R1B haplogroup is the most common Y haplogroup in Europe today with the largest concentration in the British Isles.[2][3]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 The Horse the Wheel and Language, how Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes shaped the Modern World. David W. Anthony
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Anthromedia. Yamnaya Pastoralists: Ancestors of Indo Europeanshttps://youtu.be/xA2WyIGXPIw?si=_Ff6Oy-VcPWYLY7R
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dan Davis History. The Yamnaya Culture | Bronze age Steppe Herders https://youtu.be/GalZLoTeU74?si=S6UCYHQIJSwuBtmY
